Introduction
Version control is a fundamental aspect of Node.js development, enabling smoother collaboration, efficient code management, and seamless rollback capabilities. In this guide, we'll explore the importance of versioning and delve into various strategies tailored for Node.js projects.
Versioning Strategies
Semantic Versioning (SemVer)
Advantages
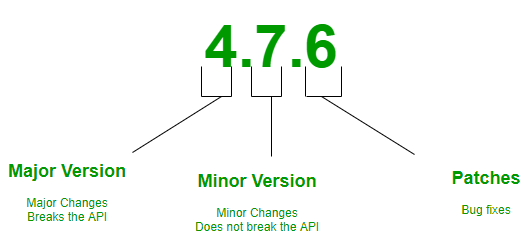
SemVer provides a structured approach to versioning, consisting of major, minor, and patch releases. This clarity aids in dependency management, as developers can easily discern the significance of each version increment. Major versions indicate backward-incompatible changes, minor versions signify backward-compatible additions, and patch versions denote backward-compatible bug fixes. This systematic approach fosters communication between developers and consumers, enhancing understanding and expectation management.
Disadvantages
Adhering strictly to SemVer principles requires discipline, as developers must accurately assess the impact of their changes on the project's compatibility. Additionally, determining whether a change constitutes a major, minor, or patch release can sometimes be subjective, leading to potential inconsistencies.
Date-based Versioning (YYYY.MM.DD)
Advantages
Date-based versioning simplifies tracking by using the release date as the version number. This approach provides a chronological sequence of releases, making it easy to identify the latest version and track the progression of updates over time. Date-based versioning is particularly suitable for projects with frequent releases or those that prioritize timeliness over semantic versioning.
Disadvantages
While date-based versioning offers a straightforward method of versioning, it may not convey information about the nature of changes within a release. Developers and consumers may find it challenging to discern whether a specific release contains major feature enhancements, bug fixes, or minor improvements solely based on the version number.
Feature-based Versioning (e.g., v1.0-login)
Advantages
Feature-based versioning incorporates feature names or identifiers into version numbers, making it easier to understand the changes introduced in a particular release. This approach enhances clarity and transparency, especially for consumer-facing applications where feature updates are prominently highlighted. Consumers can quickly identify which features or functionalities have been added or modified in each release.
Disadvantages
Feature-based versioning may lead to bloated version numbers, especially in projects with a large number of features or frequent updates. Additionally, as the number of features increases, maintaining a coherent versioning scheme becomes more challenging, potentially resulting in version number ambiguity or inconsistencies.
Practical Examples
- Implementing a New Feature and Bumping the Minor Version
// Before:
"version": "1.2.3"
// After:
"version": "1.3.0"
- Fixing a Bug and Releasing a Patch Version
// Before:
"version": "1.2.3"
// After:
"version": "1.2.4"
Conclusion
In Node.js development, version control is indispensable for maintaining a stable and scalable codebase. By adopting a suitable versioning strategy and leveraging tools like Git, developers can streamline collaboration, ensure code integrity, and enhance project maintainability.
Let's ensure our Node.js projects sail smoothly through versioning seas, with clarity, confidence, and collaboration at the helm. Happy coding!
Connect with us:
Hashnode: https://hashnode.com/@Nehal71
Twitter : https://twitter.com/IngoleNehal

