Introduction
Node.js is a powerful runtime environment that allows you to build scalable and efficient server-side applications using JavaScript. In this guide, we'll walk through the process of creating a server in Node.js from scratch. By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a solid understanding of how to set up a basic server, handle HTTP requests, and build RESTful APIs.
Fs module
In Node.js, the fs (file system) module provides an API for interacting with the file system on your machine. It allows you to perform various file-related operations such as reading, writing, updating, and deleting files and directories. In this blog, we'll explore the capabilities of the fs module and learn how to use it effectively in your Node.js applications.
Certainly! The provided code snippet utilizes the Node.js fs (file system) module and the os (operating system) module to perform file system operations and retrieve information about the system's CPUs, respectively. Let's break down the code and explain it in detail:
const fs = require('fs'); // Importing the file system module
const os = require('os'); // Importing the operating system module
fs: Thefsmodule in Node.js allows you to perform file system operations such as reading, writing, and manipulating files and directories.os: Theosmodule provides a way of interacting with the operating system. In this code, we're using it to retrieve information about the system's CPUs.
console.log(os.cpus().length); // Print the number of CPU cores
os.cpus(): This method returns an array containing information about each CPU core on the system. We use.lengthto determine the number of CPU cores available.
fs.writeFileSync("./file.txt" , "Hello World"); // Blocking file write operation (Synchronous)
fs.writeFileSync(): This method writes data to a file synchronously, meaning it blocks the execution of the script until the operation is complete. In this case, it writes the string "Hello World" to a file namedfile.txtin the current directory.
fs.writeFile("./file.txt" , "Hello World" , (err) => {
console.log();
}); // Non-blocking file write operation (Asynchronous)
fs.writeFile(): This method writes data to a file asynchronously, meaning it does not block the execution of the script. It takes a callback function that is executed once the operation is complete or encounters an error. In this case, it also writes the string "Hello World" to thefile.txtfile, but asynchronously.
Building a Basic HTTP Server

Introduction
Node.js allows you to create powerful servers easily using its built-in HTTP module. In this blog, we'll explore how to build a basic HTTP server in Node.js using the http module. We'll also demonstrate how to handle HTTP requests and log them to a file using the fs module.
const fs = require('fs');
const http = require('http');
const myServer = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// Server logic goes here
});
const PORT = 8000;
myServer.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server is listening on port ${PORT}`));
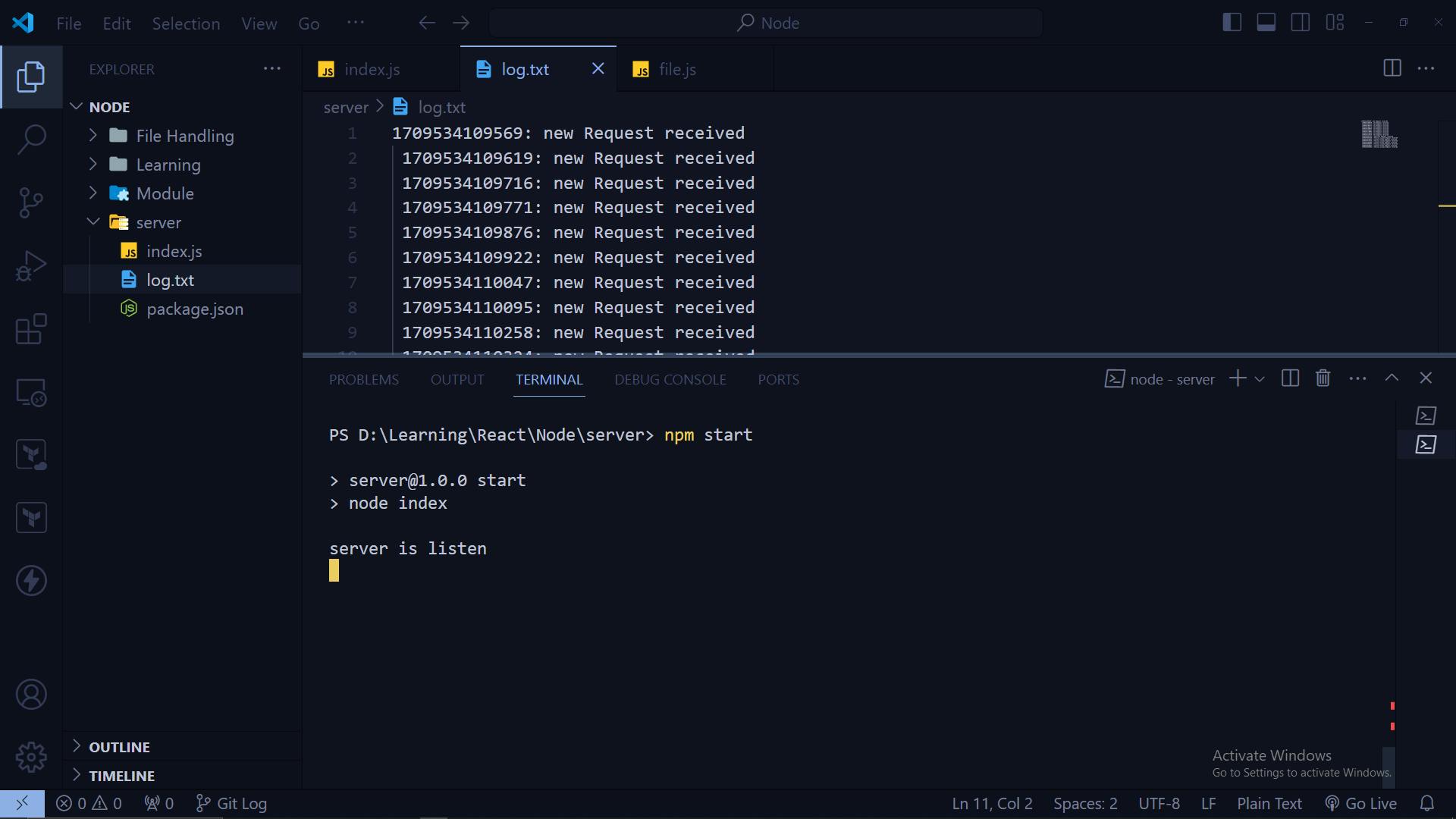
In this code, we create an HTTP server usin the http.createServer() method and specify a callback function to handle incoming requests.
HomePage
About Page
Contact-us
Another page (404 not found)
Handling HTTP Requests
Next, we'll define the logic to handle different HTTP requests based on the requested URL.
const myServer = http.createServer((req, res) => {
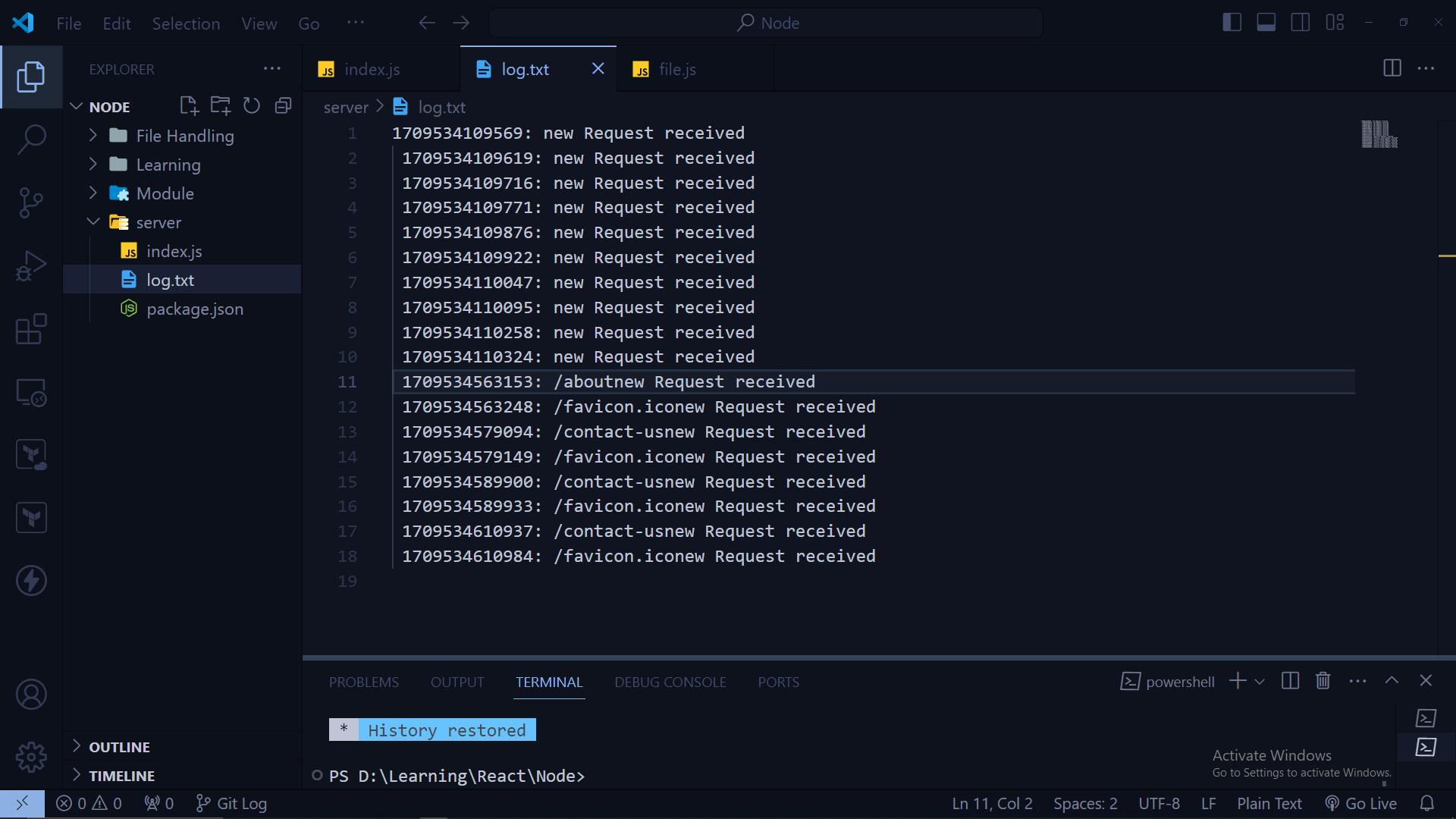
const log = `${Date.now()}: ${req.url} - New request received\n`;
fs.appendFile('log.txt', log, (err) => {
if (err) console.error('Error logging request:', err);
});
switch (req.url) {
case '/':
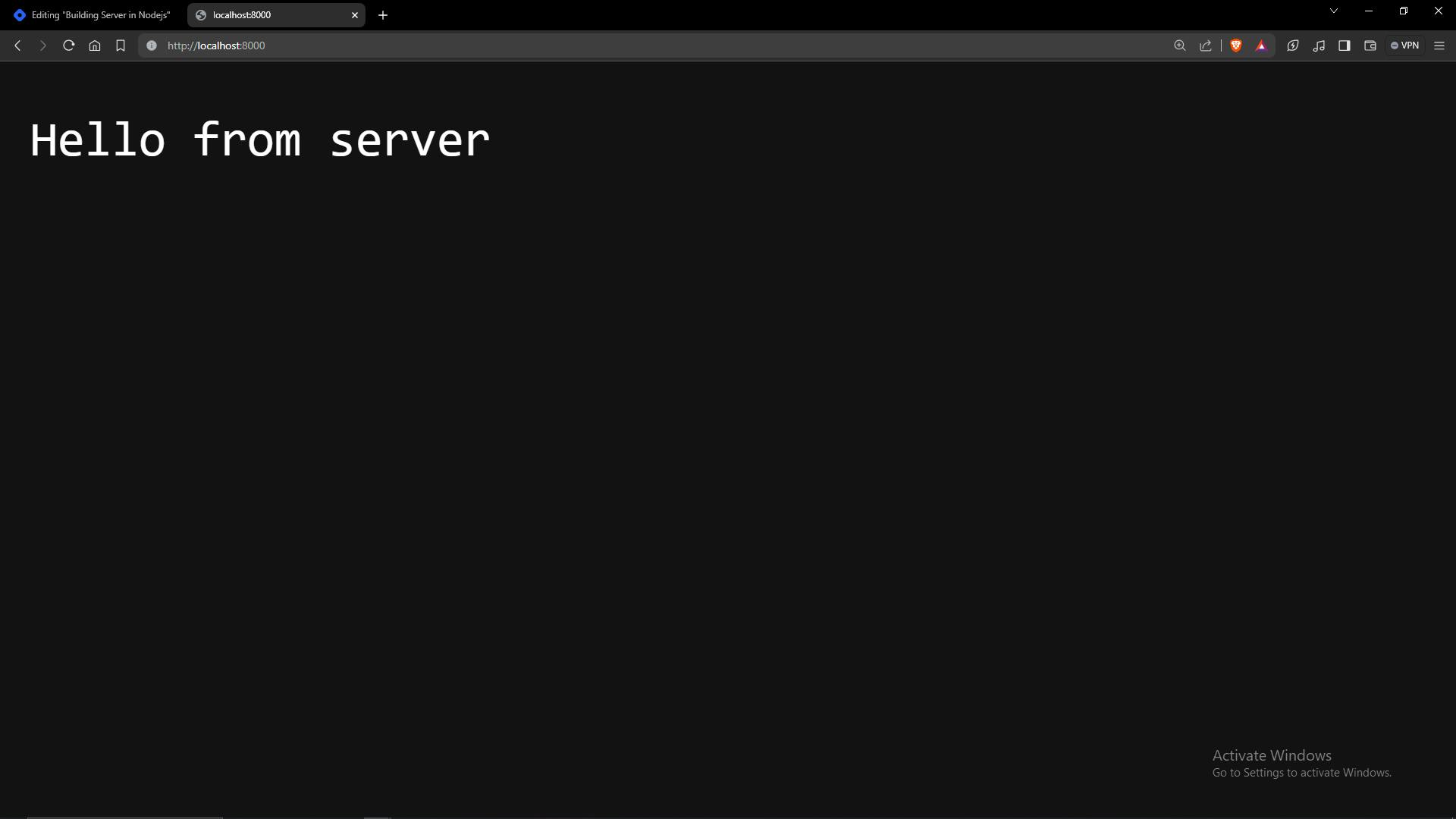
res.end('Hello from the server');
break;
case '/about':
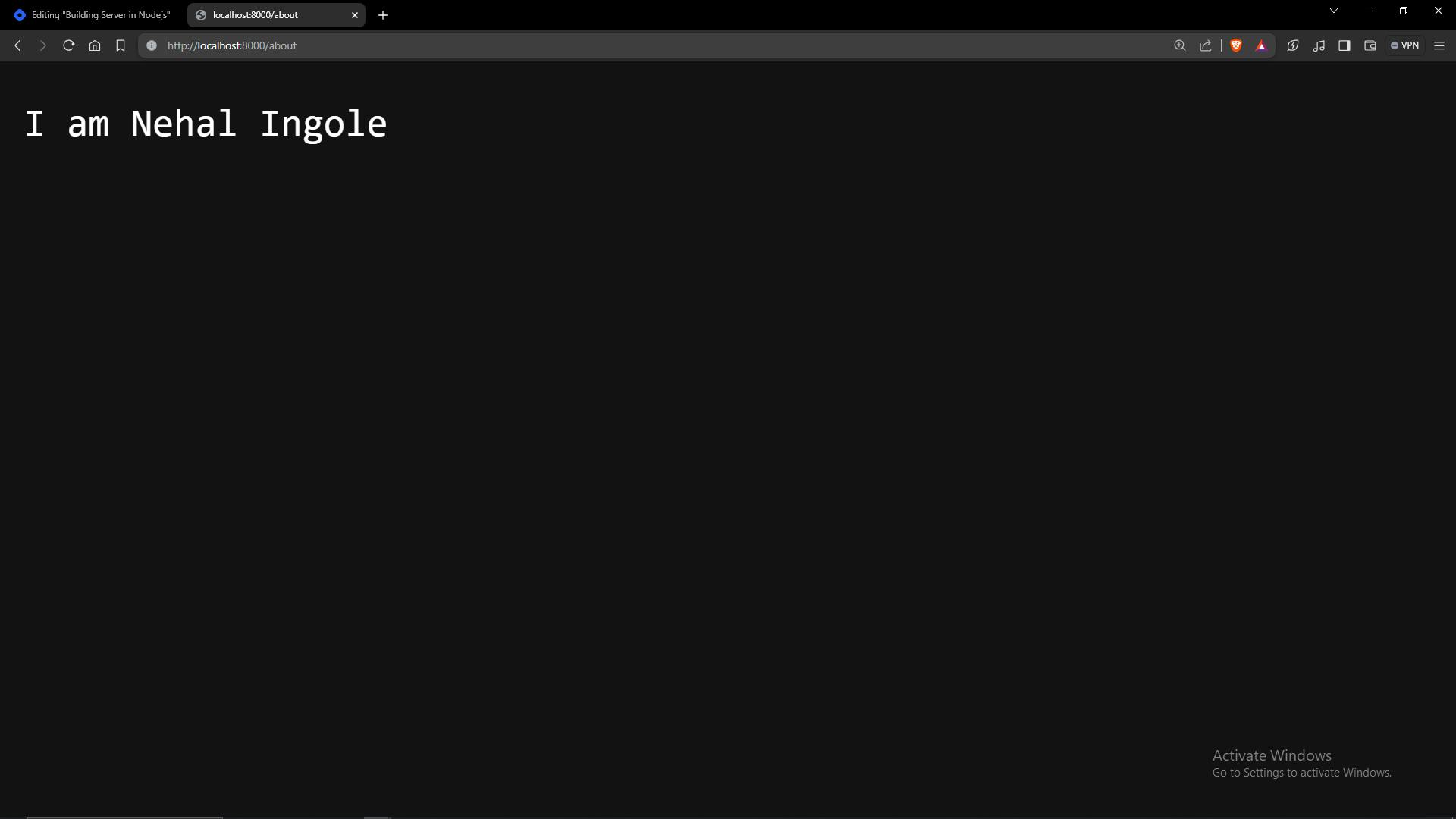
res.end('I am Nehal Ingole');
break;
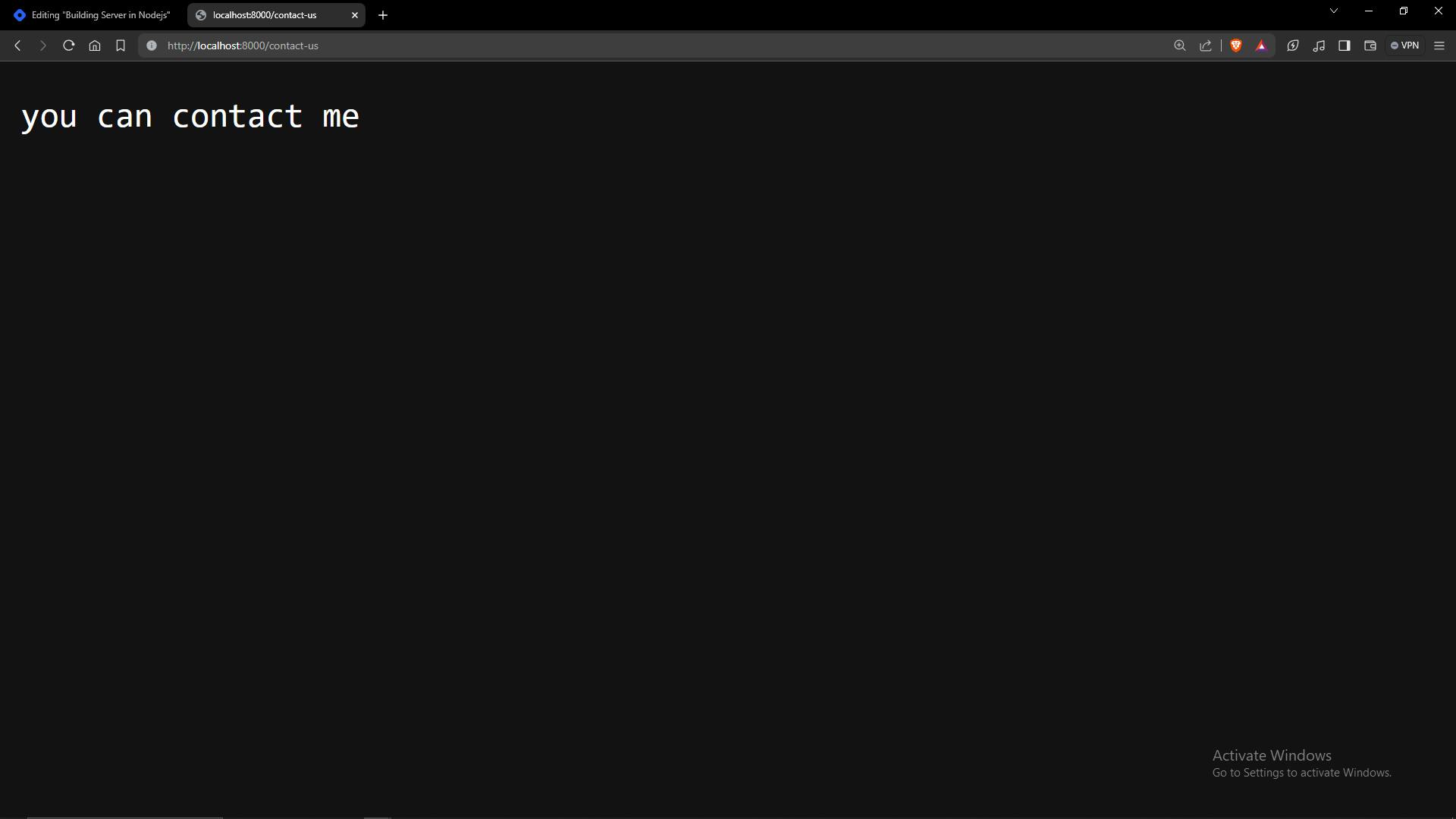
case '/contact-us':
res.end('You can contact me');
break;
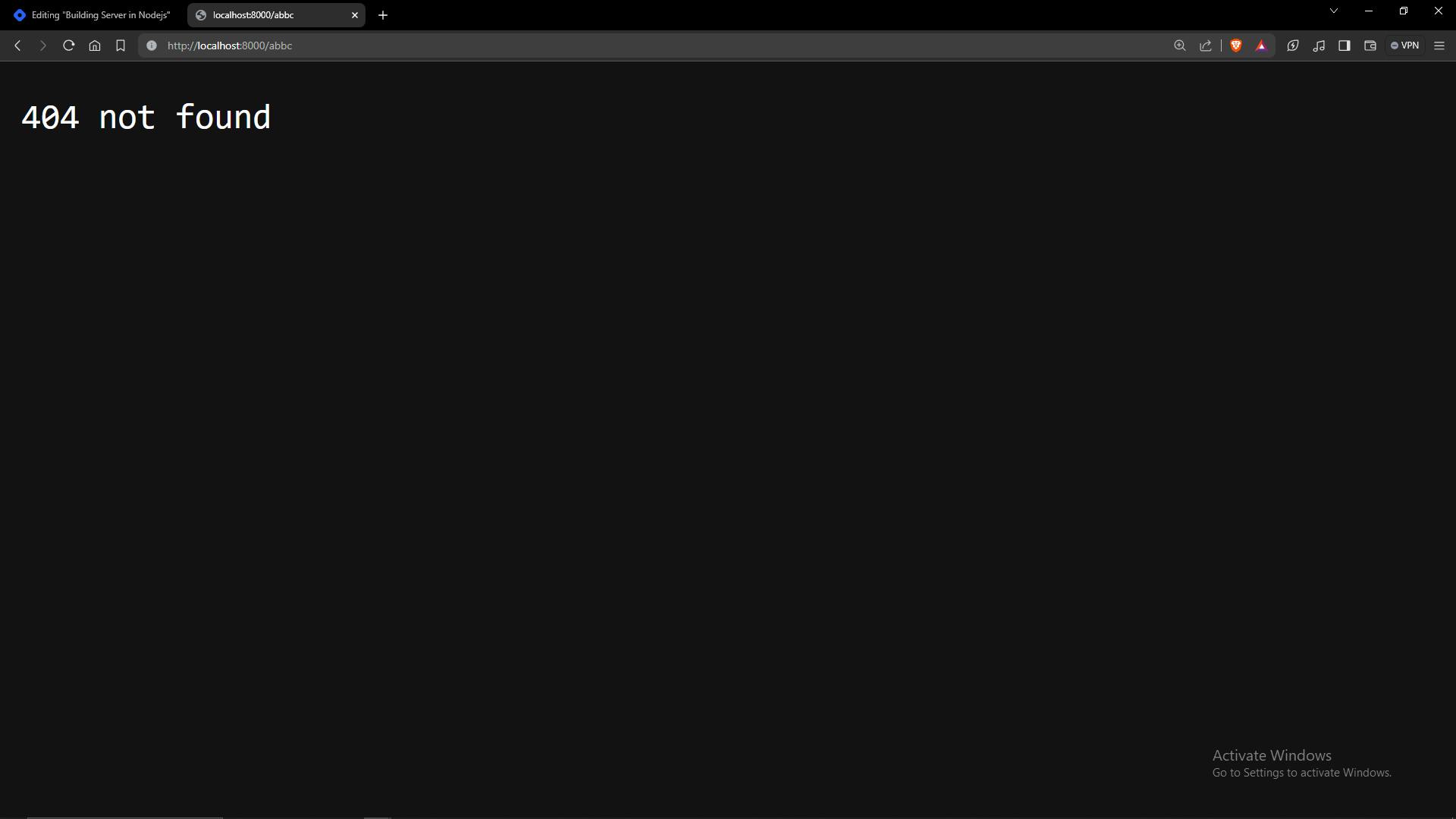
default:
res.end('404 Not Found');
}
});
This code appends a log entry to a file (log.txt) for each incoming request and handles different URLs with appropriate responses.
Logging Requests to a File
We use the fs.appendFile() method to log each request to a file named log.txt. This helps in tracking and debugging incoming requests.
Conclusion
In this series, we've taken a deep dive into the world of Node.js, exploring its vast capabilities and functionalities. We've covered everything from building basic servers to mastering advanced concepts like streams and asynchronous programming. Whether you're a beginner looking to get started with Node.js or an experienced developer aiming to sharpen your skills, we hope this series has provided valuable insights and knowledge to help you succeed in your Node.js journey.
Thank you for joining us on this exhilarating journey through the realm of Node.js! We've covered a lot of ground, but remember, learning is a continuous process. Keep experimenting, keep exploring, and keep pushing the boundaries of what you can achieve with Node.js. Stay tuned for more exciting content, and until next time, happy coding!
Connect with us:
Hashnode: https://hashnode.com/@Nehal71
Twitter : https://twitter.com/IngoleNehal

